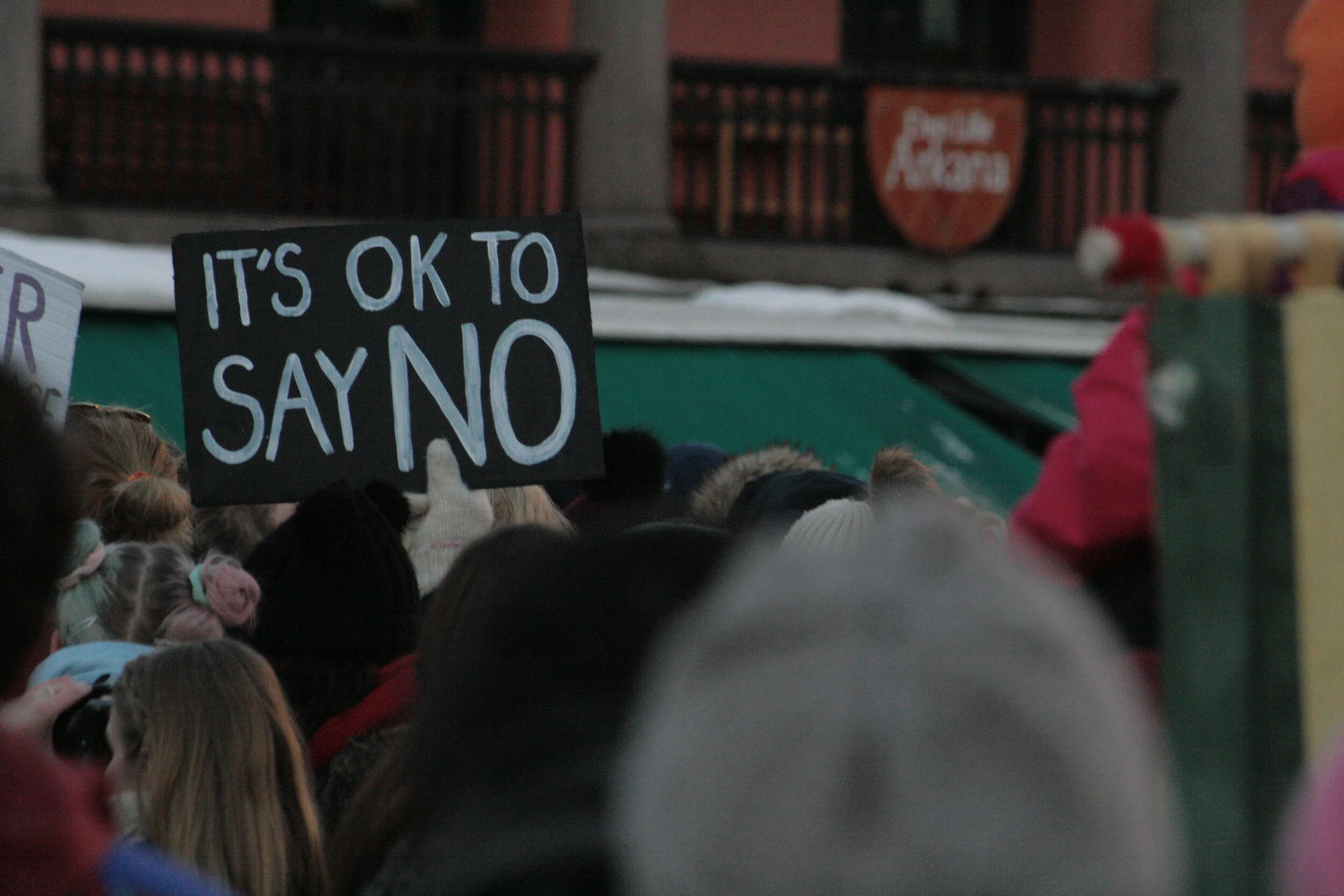Filtered by Category: Litigation
![More Steps Involved in Making a Document Production]()
Lawyers also need to make sure that documents are coded for privilege and redacted, even if the documents are not responsive to a document request. This is because a document may be produced because it is the family member of (attached to or embedded in) another document that is responsive to a document request and is thus subject to production.
Read More
![Drafting Interrogatories]()
Interrogatories may also be useful to define what an adversary’s claims or defenses are. To that end, a party may ask an opponent to identify each fact that supports its claims or each instance of misconduct that it alleges. Although a party may be able to ask the same questions to a party at a deposition, an interrogatory is more likely to get a useful response and less likely to get an “I don’t know offhand” or some other incomplete answer.
Read More
![Responding to Document Requests]()
Often, parties will make compromises in discovery to avoid the expense and uncertainty of going to court. For example, if a party believes it is entitled to all of a company’s financial records and the recipient believes it is entitled to none, the two may compromise and the recipient may agree to produce some specific financial records.
Read More
![Enforcement of Judgments]()
If a defendant does not voluntarily pay a judgment, the plaintiff must find assets that belong to the defendant and collect them. This process may be easy for some defendants if they have well-known assets or if details about their bank accounts were shared in discovery. But for others, plaintiffs may need to hire an investigator or use public records (like property records or vehicle registrations) to find assets.
Read More
![Discovery to Aid Litigation Outside of the United States]()
The American legal system allows litigants to compel the production of far more evidence before trial than many other systems. And it does not limit this power to proceedings taking place within the United States. Instead, pursuant to statutes like 28 U.S.C. § 1782 or CPLR 3102(e), litigants can ask American courts to compel discovery for use in proceedings abroad.
Read More
![Employment Discrimination and Harassment Claims]()
When determining whether to settle, it can be difficult for employees and employers to calculate an appropriate amount for the employer to pay. Unlike a contract dispute, where an agreement can set forth an amount due, there is no natural number that can compensate an employee for discrimination.
Read More
![Courtesies to Adversaries]()
The client may believe that, if her lawyer says “too bad” to an adversary who is about to go off on vacation and therefore cannot respond to a complaint, the lawyer may be doing justice by helping her win quickly and cheaply. But the truth is that the opposing counsel will likely be able to ask the court for an extension anyway and then be less willing to give extensions in return when the client’s counsel wants them. It’s a lose-lose situation.
Read More
![Specialized Commercial Courts]()
Sophisticated businesses often agree to resolve their disputes through private arbitration instead of by going to court. Arbitration has numerous advantages, such as being confidential instead of public and being generally less expensive. But another advantage is that the parties can provide input on the selection of their arbitrator and thus can select an arbitrator and a forum that is well-suited for commercial disputes.
Read More
![The First Steps in How Document Productions Get Made]()
How does someone take thousands of emails and decide which get produced? And are there a bunch of complicated rules and procedures that would surprise someone who doesn’t do this all the time? The answers are “a variety of ways” and “yes.”
Read More
![Pro Hac Vice]()
Why should you consider having a lawyer get admitted pro hac vice instead of just hiring local counsel to represent you? Because if you already have a relationship with a lawyer you trust, you may feel more comfortable with them representing you that with a stranger. This is especially true if you believe that your lawyer is particularly skilled or capable. And if you use your existing lawyer, you don't need to pay to bring a new lawyer up to speed on facts of the case if your existing lawyer already knows the facts.
Read More
![Deposition Designations]()
Witnesses swear to tell the truth at the start of their depositions, just as they do when they testify in court. And violating that oath is technically a crime, just as it would be for lying in court. And a court reporter makes a verbatim transcript of the deposition, which allows lawyers to submit the exact same testimony at trial.
Read More
![Answers]()
Answers are usually relatively inexpensive documents to draft because they do not need to be well-crafted narratives that persuade people of the defendant’s innocence. Defendants have other opportunities in a lawsuit to explain their story, such as in motions to dismiss the case and at trial.
Read More